
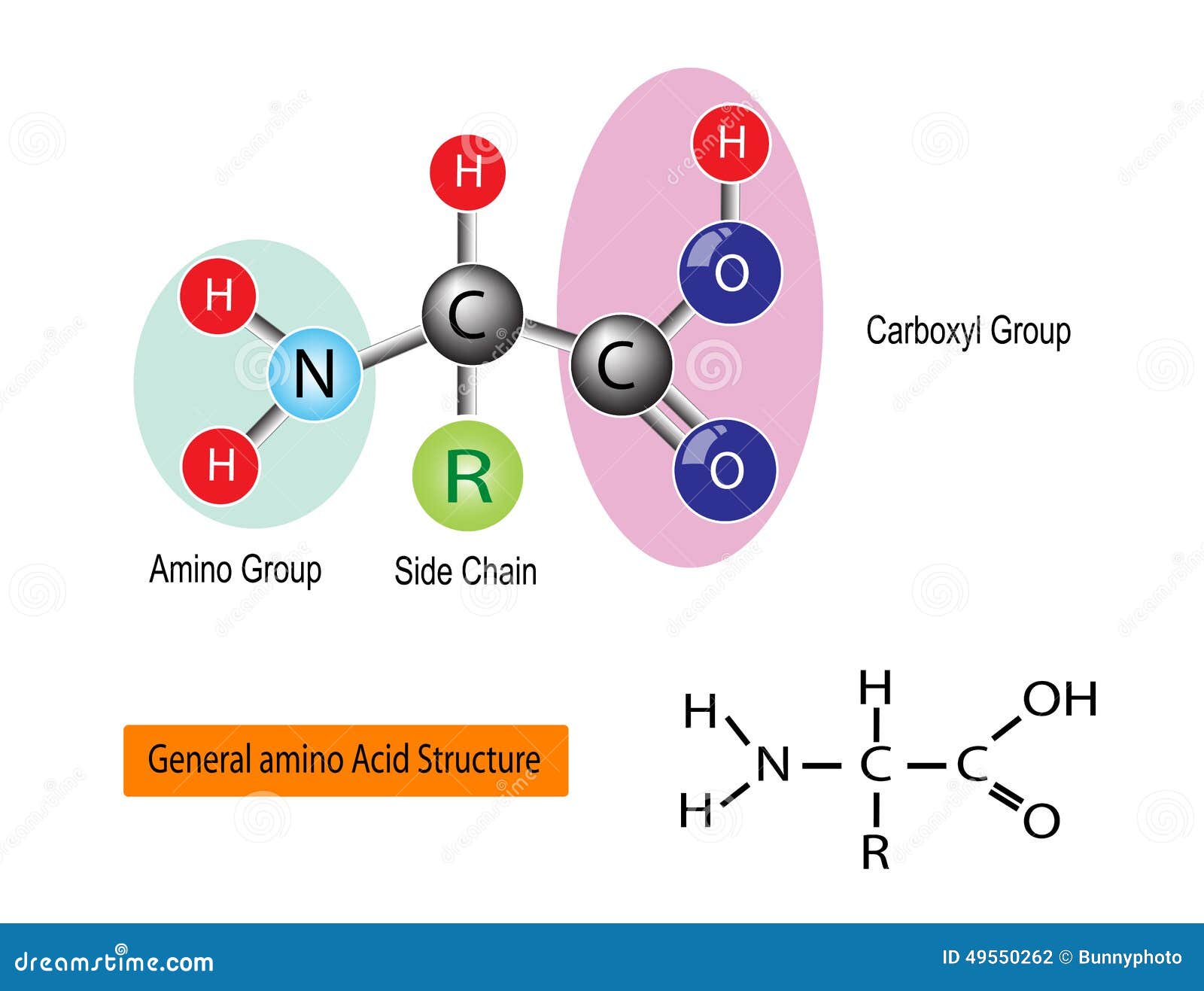
In vivo, each amino acid is added to the amino-terminal of one amino acid to form a peptide chain. As peptide chains form between joining of the primary structure of amino acids, they may enlarge to become an oligopeptide when there are between 10 to 20 amino acids in the chain. Peptides are named based on the number of amino acid residues in the sequence. Sequential covalent bonds with additional amino acids yield a peptide chain and the building block of proteins.
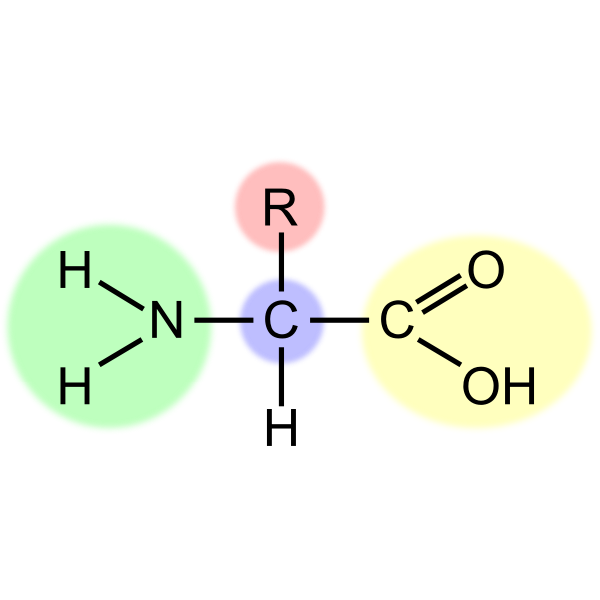
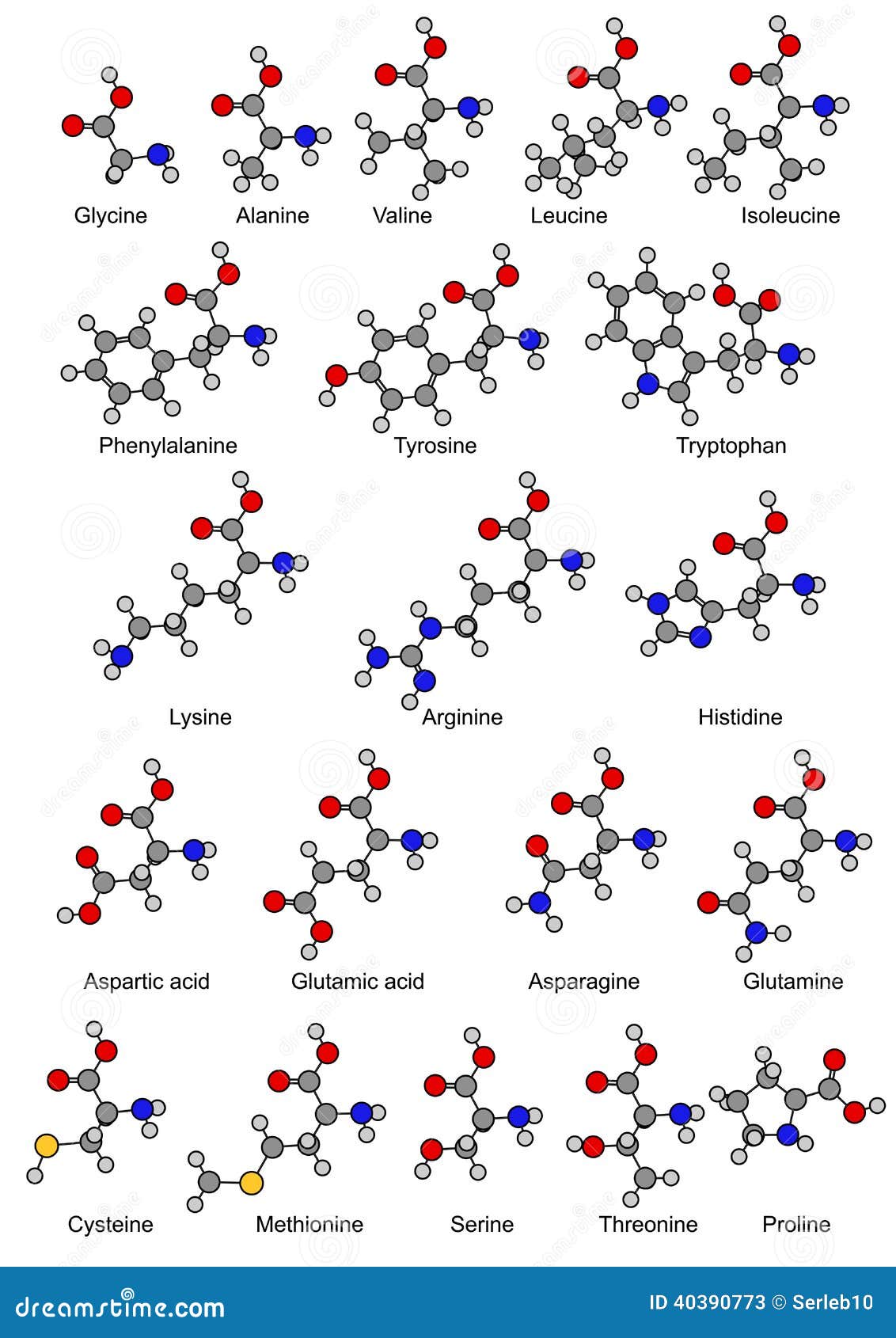
A peptide is a short string of 2 to 50 amino acids, formed by a condensation reaction, joining together through a covalent bond. Peptides play an essential role in fundamental physiological processes and are necessary for many biochemical processes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
